Need a topic for an informative speech? You're in the right place. We've compiled 150+ ideas for informative speeches so you can be inspired and choose the right one for you.
In addition to a long list of ideas, this article will also give you guidance on choosing your topic, structuring your speech, and example slides that you can use for your speech.
Browse by category, find topics that resonate with you, and start working on a speech that will be engaging for you and your listeners.
{toc}
How to choose a speech topic
Picking the right topic will make everything else easier, as you prepare for your speech.
Try to pick a topic that meets these criteria:
- You're interested in the subject matter – You're going to spend hours researching and practicing this speech. Pick something you actually want to learn about, and that curiosity will come through when you talk. (Try to find the stories and hidden gems that will make your audience lean in while you talk)
- It's appropriate for your audience – Consider what your listeners already know and what will challenge them without losing them. A topic that's too basic will bore them; one that's too complex will confuse them.
- It fits your setting – If your venue has a screen and speakers, you can use videos and detailed visuals. If not, choose a topic you can convey effectively through words alone.
- You can find (or create) strong visuals – The best informative speeches are backed by solid research and enhanced by compelling images or videos. If you can't find quality materials to support your topic, consider a different one.
How to prepare your informative speech presentation
Now that you’ve chosen your speech topic, it’s time to prepare the presentation that will accompany you on the stage as you speak. By following the following five steps, you’ll make a presentation that effectively guides both you and your viewers through the key points of your speech.
- Research thoroughly
- Adhere to the 6 C’s of informative speaking
- Find a suitable platform for creating your presentation
- Ask for a peer review
1. Research thoroughly
Your task is to compose a speech that informs, so to start, research your topic until you know it like the back of your hand. Use credible sources, not just random blogs you find on Google (Google Scholar is an excellent choice). As you study the subject matter, note all the pertinent data, and create an outline that presents information in smooth, contextual flow.
2. Follow the 5 C’s of informative speaking
The 6 C’s of informative speaking help you deliver (and your audience absorb) the message effectively. A speech that adheres to the 6 C’s is:
- Clear: Use clear phrasing that everyone understands.
- Colorful: Enliven your speech with color to keep the viewers’ attention.
- Concrete: Eliminate ambiguities and deliver concrete information that leaves no room for misinterpretation.
- Correct: If you present something as a fact, make sure you’ve triple-checked its accuracy (Don't get caught presenting AI hallucinations!).
- Concise: Keep the written content in your slides and your speaking notes as short as possible.
3. Find a suitable platform for creating your presentation
Try using one of thebest AI presentation maker to help you tackle your slides quickly and without a ton of manual effort. For example, Plus AI does all the heavy lifting and lets you generate professional presentations from a prompt, then helps you edit and format the slides quickly. With these tedious tasks out of the way, you can focus your time on the content of the speech.
4. Ask for a peer review
Get your fellow student or coworker to review your presentation and give you their notes. You can even rehearse the speech with them to get some feedback on the delivery. Such a rehearsal should help you refine your speech (and slides) before the big day.
Ideas for easy informative speech topics
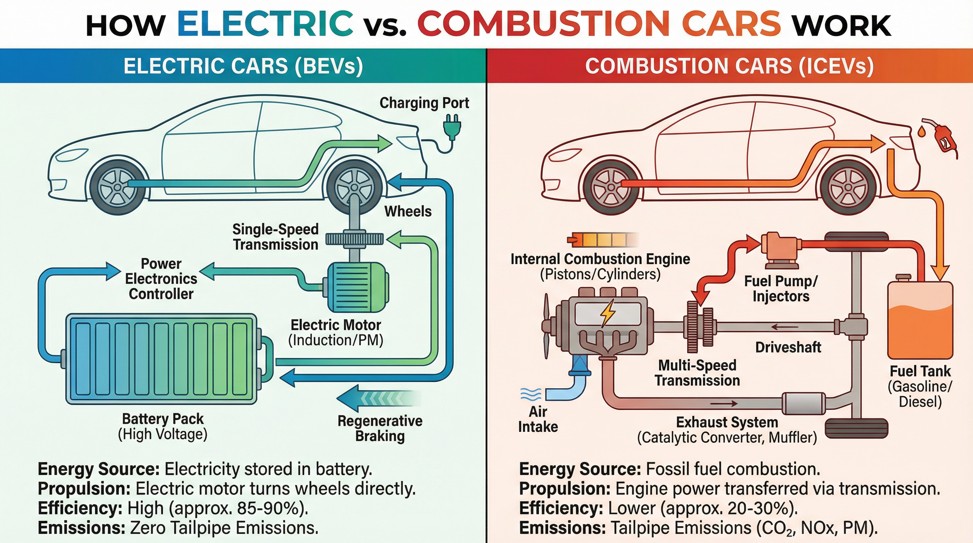
These topics work well for classroom presentations or practicing public speaking. They don't require exhaustive research, but you'll want to use engaging visuals and keep your talking points concise.
- How electric cars work – Electric cars are everywhere, but most people don't know how they actually function. Use diagrams to explain the key components, then compare how they operate versus traditional gas-powered vehicles.
- The most popular sports around the world – Baseball is America's pastime, but it's also the most popular sport in Japan, Taiwan, and the Dominican Republic. Organize your presentation by sport and include surprising statistics about global fandom.
- How the food you eat becomes energy – Explain the basics of digestion and metabolism in a way that's accessible and visual. Use infographics to show what's happening inside your body.
- How your phone tracks your location – Walk through how GPS satellites, cell tower triangulation, Wi-Fi positioning, and apps work together to pinpoint where you are. This is a great entry point into bigger conversations about privacy, data collection, and how much your phone knows about your daily routine.
- How to improve your sleep – Most people don't get enough sleep, making this useful for almost any audience. Go beyond generic advice like "put your phone away" and dig into the science: how light affects melatonin, why consistency matters more than duration, and what the research says about sleep stages. Each slide can focus on one actionable habit backed by data.
- How to build a basic budget – Walk through the fundamentals of tracking income and expenses, setting savings goals, and avoiding common mistakes. Use real examples instead of generic stock images.
- What happens when you recycle – Most people toss items in the recycling bin without knowing what happens next. Trace the journey of aluminum, plastic, and paper from curbside pickup through sorting facilities to their second life as new products. Include the surprising percentage of "recycled" items that actually end up in landfills.
- How streaming algorithms decide what you watch – Explain how recommendation systems work on Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube. This is a relatable entry point into how AI shapes daily life.
- How airplanes stay in the sky – The physics of flight is fascinating and widely misunderstood. Use diagrams to explain lift, thrust, drag, and weight in simple terms.
- Types of extreme weather – Hurricanes, tornadoes, droughts, and atmospheric rivers are becoming more frequent. Cover their characteristics, causes, and tips for staying safe.
- The greatest natural disasters in history – Humans are drawn to stories of catastrophe. Go beyond dramatic photos and focus on causes, casualties, and what we've learned about resilience.
- The psychology of pricing – Explain why $9.99 feels cheaper than $10, how anchoring works, and why restaurants put expensive items at the top of menus. This is a fun, practical topic that changes how your audience sees every price tag.
- How noise-canceling headphones work – Explain active noise cancellation using destructive wave interference. Use diagrams to show how microphones detect ambient sound and speakers produce inverse waves. A great topic for anyone interested in audio, physics, or everyday technology.
- How to build a 72-hour emergency kit – Floods, wildfires, and earthquakes can displace people without warning. Base your presentation on FEMA guidelines and show how to actually use each item.
- First aid skills everyone should know – Cover the basics of CPR, choking response, and wound care. Instructional videos are the best visual aid here.
- How the internet actually works – Explain servers, IP addresses, DNS, and data packets in plain language. Most people use the internet for hours every day without understanding what's happening behind the scenes. Use analogies to make abstract concepts concrete.
- How vaccines work – A timely, practical topic. Explain how vaccines train the immune system and address common misconceptions with clear visuals.
- How credit scores work – Most young adults don't understand credit until it's too late. Explain what affects your score, why it matters, and how to build credit responsibly.
- The world's most unusual buildings – Architecture can be stunning and strange. Highlight key facts like the architect, materials, and construction timeline alongside striking images.
- What makes a city "smart"? – Explain how cities like Singapore and Amsterdam use data and technology to manage traffic, energy, and public services.
- The world's longest bridges – Cover location, span, construction methods, and history. Save the longest bridge for your final slide to end with impact.
- How to plan a gap year trip – Help your audience evaluate destinations by covering attractions, costs, visa requirements, and safety considerations.
- How maps have shaped history – From Ptolemy's ancient atlas to the Mercator projection to Google Maps, cartography has influenced exploration, colonization, warfare, and how we understand the world. Show how maps can distort reality and why maps matter.
- How search engines rank results – Explain the basics of SEO and how Google decides what shows up first. Useful and demystifying for any audience.
- The science of habit formation – Cover how habits form in the brain and evidence-based strategies for building good ones and breaking bad ones.
- Why we procrastinate (and how to stop) – Explain the psychology behind procrastination—it's not laziness, it's often emotional regulation. Cover strategies that actually work, like implementation intentions and temptation bundling, backed by research.
- How money moves through the economy – Trace how a dollar bill circulates from consumers to businesses to banks to government and back. A simple but powerful way to explain economic concepts like velocity of money, fractional reserve banking, and the role of the Fed
- How body language affects first impressions – Cover the do's and don'ts with images or video clips. Useful for interviews, networking, and everyday interactions.
Ideas for intermediate informative speech topics
- How screen time affects kids and teens – Present findings from multiple studies on the relationship between screen time and well-being. Include perspectives from psychologists, parents, and young people themselves.
- Why adults are obsessed with superheroes – Explore theories behind our cultural fascination with superhero stories—escapism, hope, and the appeal of clear moral lines.
- The four main parenting styles – Walk through authoritarian, authoritative, permissive, and neglectful parenting. Cover the characteristics, pros, and cons of each.
- How misinformation spreads online – Trace how false stories go viral, from initial posting through sharing networks to mainstream coverage. Explain the psychological reasons people share misinformation (it's not just gullibility) and what platforms are—or aren't—doing to stop it.
- What are "blue zones"? – Tour the five regions where people live the longest: Okinawa, Sardinia, Nicoya, Ikaria, and Loma Linda. Explore the lifestyle factors that may explain their longevity—diet, movement, community, purpose—and what the rest of us can learn from them. Then reveal how data issues may be the main driver of "long lives."
- The psychology of decision-making – Explain cognitive biases like anchoring, confirmation bias, and loss aversion, and how they shape everyday choices.
- How advertising manipulates you – Break down the psychological tactics advertisers use—scarcity, social proof, emotional appeals—and how to recognize them.
- How cuisine shapes culture – Explore how recipes and food traditions reflect a society's values, history, and identity.
- The history and science of addiction – Explain how addiction works in the brain, how our understanding has evolved, and what treatments are most effective.
- What's driving the mental health crisis? – Present research on contributing factors: social media, economic insecurity, loneliness, academic pressure, and reduced stigma leading to increased diagnosis.
- How social media affects mental health – Cover both positive and negative impacts, supported by research. Include expert perspectives to add depth.
- What is a large language model (LLM)? – Explain how tools like ChatGPT work, and address common questions: Can they reason? Are they conscious? Could they become AGI?
- The ethical dilemmas of AI – Cover bias in training data, job displacement, autonomous weapons, deepfakes, and questions of accountability when AI makes harmful decisions. Present multiple perspectives and give your audience space to form their own views.
- How blockchain actually works – Use a Bitcoin transaction as a concrete example to walk through each step. Cover applications beyond cryptocurrency and weigh the pros and cons.
- Why eyewitness testimony is unreliable – Explain the science of memory and why confident witnesses are often wrong. Use real cases where eyewitness errors led to wrongful convictions.
- The future of transportation – Explore emerging technologies like eVTOL aircraft, hyperloop, and new micromobility options. Explain what problems they're trying to solve.
- What's causing climate change and what can we do? – Cover the science (greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, feedback loops), the biggest contributors by sector and country, and the range of solutions from individual action to policy to geoengineering. Use current data and projections.
- Cities that could be underwater by 2050 – List at-risk cities, explain the projections, and discuss what's being done to prepare or adapt.
- How to spot propaganda – Teach your audience to identify manipulation tactics in media. Use real examples while staying clear of partisan flashpoints.
- How the prison system works in the US – Explain the basics of arrest, bail, plea bargaining, sentencing, incarceration, and parole. Compare US incarceration rates to other developed countries and examine the factors that explain the difference.
- How the Electoral College works – Explain the full process from Election Day to certification, including cases where the popular vote winner lost the presidency.
- How lobbyists influence legislation – Demystify how lobbying works, who does it, and how it shapes the laws that affect everyday life.
- How languages die – Explain what causes languages to go extinct, languages that have already gone extinct, and which ones are most endangered.
- Comparing systems of government – Use specific countries as examples to explain how different governments form, pass laws, and function day to day.
- The state of democracy worldwide – Use maps and data to show where democracy is strengthening, where it's declining, and what factors are driving the changes.
- The deadliest conflicts in history – Rank major wars and conflicts by casualties, discuss root causes, and explore what lessons we can draw for the future.
- How social movements succeed (or fail) – Examine historical movements—civil rights, labor, suffrage, environmental—and identify what factors predict success: organization, leadership, tactics, timing, and public opinion shifts.
- The economics of healthcare – Explain why US healthcare costs so much compared to other developed countries, what single-payer and multi-payer systems look like, and the trade-offs involved in different approaches to reform.
- How criminal profiling works (and doesn't) – Explain the methods FBI profilers use, the famous cases that built the field's reputation, and the research showing its accuracy is far lower than pop culture suggests.
- How cults recruit and control members – Outline the psychological tactics cults use: love bombing, isolation, thought-terminating clichés, and escalating commitment. Explain who is vulnerable and why smart, educated people get drawn in.
- The history of surveillance – From informants in ancient Rome to the Stasi to the NSA, trace how governments have monitored their citizens. Discuss the tension between security and privacy, and how technology has changed the equation.
- How forensic science has evolved – Cover fingerprinting, DNA analysis, ballistics, and digital forensics. Address the limitations and errors that have led to wrongful convictions, and how the field is becoming more rigorous.
Ideas for complex informative speech topics

These topics are geared toward a high school or university-level audience. They cover sophisticated theories and technologies at the forefront of research. Do your best to break up dense content with strong visuals, videos, and discussion.
- Gene therapy: how it works and where it's headed – Explain the science, delivery methods, and current applications. Use statistics to show effectiveness across different diseases.
- What is CRISPR gene editing? – Describe the mechanism behind this technique, its practical applications, and the ethical controversies surrounding it.
- How mRNA vaccines work – Walk through the full process: how mRNA is designed, encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles, delivered to cells, and translated into proteins that trigger immune response. Compare to traditional vaccine approaches and explain why mRNA technology could revolutionize medicine beyond COVID.
- AI in healthcare: current uses and future potential – Show how AI is being used in diagnostics, drug discovery, and patient care. Discuss where it's headed and what concerns remain.
- How nanotechnology is changing medicine – Cover current applications, ongoing research, and the tools used in production. Address both the promise and the concerns.
- How the James Webb Space Telescope works – Explain JWST's infrared capabilities, its 18 hexagonal mirror segments, its sunshield the size of a tennis court, and its orbit at L2. Show recent images and explain what they've revealed about early galaxies, exoplanets, and stellar formation.
- The future of space exploration – Analyze past missions, current projects, and what's on the horizon. What will motivate continued exploration, and what constraints remain?
- Can we make Mars habitable? – Present the science of Mars's environment, the technology needed, and current mission plans. Let your audience weigh in on feasibility.
- What is consciousness? – Survey philosophical and scientific approaches to the mind-body problem. Cover dualism, physicalism, and panpsychism, and discuss why consciousness remains one of the hardest problems in science.
- The return of supersonic flight – Compare current projects like Boom to the Concorde. Explain why supersonic travel failed before and whether it can succeed now.
- What is technological singularity? – Define the concept, trace its intellectual history from von Neumann to Kurzweil, and present competing views on whether superintelligent AI is possible, imminent, or dangerous. Discuss what it would mean for humanity if exponential AI improvement actually occurred.
- The causes of political polarization – Explore structural factors like gerrymandering and media algorithms. Stay balanced and leave room for discussion.
- How gerrymandering shapes elections – Use maps and real examples to show how redistricting affects political outcomes. Include examples from both parties.
- The psychology of radicalization – Explain the pathways by which ordinary people adopt extremist views: grievance, identity, group dynamics, online echo chambers. Cover deradicalization efforts and what research says about their effectiveness.
- What is dark matter? – Explain what we know (and don't know), the evidence for its existence, and the challenges in studying it.
- How the placebo effect works – Describe the neurophysiology behind it and its applications in medicine and research.
- Animal intelligence: what we've learned – Rank animals by cognitive ability and explain how intelligence is measured. Use videos of animal behavior to bring it to life.
- Species on the brink of extinction – Detail populations, habitats, and the factors driving decline. Cover conservation efforts and their effectiveness.
- The future of energy storage – Survey battery technologies beyond lithium-ion: solid-state, sodium-ion, flow batteries, hydrogen, and gravity storage. Explain why storage is the bottleneck for renewable energy and what breakthroughs would change the equation.
- Habitable exoplanets: what we've found – Present the most promising candidates, how they were discovered, and what makes a planet potentially habitable.
- The search for extraterrestrial life – Cover past and present efforts, from SETI to astrobiology. Address UFO sightings and what the evidence actually shows.
- The gut-brain connection – Explain how the microbiome influences mental and physical health, with visuals showing the biological pathways.
- Climate change models and predictions – Walk through the science behind current projections and what different scenarios mean for coastlines, ecosystems, and economies.
- How epidemiologists model disease spread – Explain SIR models, R0, herd immunity thresholds, and how assumptions about behavior affect predictions. Use COVID as a case study showing where models succeeded and failed.
- Preparing for the next pandemic – Share lessons from past outbreaks and the strategies most likely to reduce future damage.
- What is quantum cryptography? – Explain the basics of quantum mechanics needed to understand it, then cover how it works and why it matters.
- Modern Monetary Theory explained – Break down the core tenets, compare to Keynesian economics, and discuss the debate around its validity.
- Inflation, recession, and stagflation – Define each, explain their causes and relationships, and use historical examples to show real-world impact.
Debate-worthy informative speech topic ideas

These topics are controversial and best suited for an adult audience. Your job is to present the facts objectively and let your audience draw their own conclusions. Use credible statistics and clear visuals to support constructive dialogue. (And if you are looking for more topics that would work well for a persuasive speech, check out other post)
- Is gentle parenting effective? – Present evidence on both sides from child psychologists and educators. Let the audience—especially parents—weigh in.
- Do video games harm children? – Share research on cognitive, behavioral, and social effects. Stick to expert evidence and invite discussion.
- Individualism vs. collectivism – Compare societies where each system dominates across metrics like GDP, happiness, and human rights.
- Should we extend human lifespan? – Present the science of aging and longevity research, then explore the ethical and societal implications if we could significantly extend healthy lifespan. Who would benefit? What would it mean for population, resources, and social structures?
- What are acceptable limits on free speech? – Survey laws in different countries, present examples of outcomes, and ask your audience where they draw the line.
- What is net neutrality and why does it matter? – Explain the concept, the laws, and the real-world implications of keeping or abandoning it.
- Is climate change natural or human-caused? – Present the science distinguishing current warming from historical cycles. Let the evidence speak.
- Should AI be used in education? – Analyze the pros and cons from a student and educator perspective. Consider both learning and assessment.
- Is AI a threat or an opportunity? – Outline what AI has already automated and what's next. Examine factors that could tip the balance either way.
- Should we colonize space? – Present the case for becoming a multi-planetary species (existential risk, resources, exploration) and against (cost, ethics of terraforming, ignoring Earth's problems). Let your audience debate.
- Does AI dehumanize creativity? – Compare AI-generated art and writing to human work. Ask whether automated creativity can still move us emotionally.
- What are deepfakes and how should we handle them? – Define them, show examples, and discuss strategies for protection and regulation.
- How should we address the mental health crisis? – Present the leading proposals, their evidence base, and their trade-offs.
- Does harm reduction work? – Review the data on harm reduction policies and let your audience grapple with the moral questions involved.
- Arguments for and against the death penalty – Present the key points on both sides, including deterrence data and wrongful conviction rates.
- Is universal basic income a good idea? – Explain how UBI would work, present evidence from pilot programs, and discuss potential benefits (reducing poverty, enabling risk-taking) and concerns (cost, inflation, work incentives).
- Gun violence in the US: causes and solutions – Present statistics, compare to other countries, and survey proposed solutions and their effectiveness.
- Can billionaires be ethical? – Break down how wealth accumulates, examine philanthropy and taxes, and let your audience debate.
- The ethics of genetic engineering – Cover current practices, potential applications, and the moral questions they raise.
- Nuclear power: risk vs. reward – Compare emissions, output, and accident risk. Calculate what it would take to meet energy needs without it.
- Should voting be mandatory? – Compare countries with compulsory voting to those without. Present arguments about civic duty, freedom, and political outcomes.
- Cultural appropriation vs. appreciation – Define the distinction, give examples, and invite your audience to share their perspectives.
- Does cancel culture work? – Examine real cases and ask whether the outcomes achieved justice or caused harm.
- When is armed intervention justified? – Compare historical cases and ask what ethical framework should guide future decisions.
- What obligations do wealthy nations have to climate refugees? – Present projections for climate displacement, current legal frameworks for refugees, and ethical arguments about responsibility and burden-sharing.
- How algorithms distort reality – Explain filter bubbles and their effects on beliefs and behavior. Discuss potential solutions.
- Assisted suicide laws around the world – Compare approaches by country, including recent expansions and ongoing controversies.
- How should we measure happiness? – Present existing frameworks like the World Happiness Report and Bhutan's GNH. Invite your audience to propose alternatives.
- Competing visions for humanity's future – Survey the major forces shaping our trajectory—climate, AI, geopolitics—and let your audience share their outlook.
Creative informative speech topic ideas
These topics focus on music, culture, and the arts. They're great for visually rich, demo-heavy, and interactive presentations.
- Art through the ages – Trace how civilizations have approached art over 5,000 years, from cave paintings to digital installations.
- The rise of AI-generated art – Show examples, explain how it works, and discuss what it means for traditional artists.
- How our taste in music has changed – Pick a decade and explore how the "best" songs of that era are viewed differently today.
- The evolution of emojis – Trace emojis from Japanese mobile carriers in the 1990s to their current status as a universal visual language. Discuss how the Unicode Consortium decides which emojis to add and the cultural politics of representation.
- Global sounds: how music differs around the world – Compare musical traditions across cultures and explore how globalization is blending them.
- Food as art – Explore how chefs elevate cooking beyond sustenance: molecular gastronomy, omakase, and Instagram-driven plating. Discuss the tension between visual appeal and taste, and whether "food art" is pretentious or genuinely creative.
- Architecture vs. engineering – Examine the tension and collaboration between aesthetics and function in iconic buildings.
- The psychology of color – Show how different colors affect mood and perception, with examples from design and marketing.
- The philosophy of comedy – Explore theories of why we laugh: superiority, incongruity, relief. Discuss how comedy norms change across cultures and generations, and where the line between funny and offensive lies.
- The history of the selfie – Trace self-portraiture from Rembrandt's self-portraits to MySpace angles to Instagram filters. Discuss what selfies reveal about identity, self-presentation, and narcissism.
- The economics of streaming – Explain how Spotify and Netflix pay creators, why the model favors some artists over others, and how streaming has changed what gets made.
- How science changed art – Trace how discoveries like perspective, photography, and digital tools transformed artistic expression.
- Art in virtual reality – Explore how VR is creating new possibilities for experiencing and creating art.
- The neuroscience of creativity – Explain what happens in the brain during creative thinking and how it differs from analytical thought.
- The art of a specific region – Do a deep dive into the artistic traditions of one culture or geographic area.
- The formula behind pop music – Analyze the structural patterns in hit songs: verse-chorus structure, the "millennial whoop," four-chord progressions, and production techniques that trigger emotional responses. Play examples and let your audience hear the formulas.
- How art conservation works – Explain the science and techniques behind preserving paintings, sculptures, and artifacts.
- How language shapes creativity – Explore how different languages influence artistic expression and connection with audiences.
- The history of the orchestra – Trace how orchestras evolved from small ensembles to the massive groups we know today.
- A guide to modern dance – Create a framework for understanding the different styles and movements within modern dance.
- How typography shapes perception – Explain why font choices matter: readability, emotional associations, and brand identity. Cover the psychology research on how typefaces influence credibility and comprehension.
- How memes become culture – Trace how internet memes have moved from 4chan inside jokes to mainstream political discourse. Discuss memetic evolution, virality, and whether memes trivialize serious topics.
- Fashion cycles: why trends repeat – Show how fashion from past decades comes back around, with visual examples.
- The science of beauty – Discuss research on facial symmetry, averageness, and other factors that influence perceptions of attractiveness.
- Breakthroughs in visual effects – Highlight the technologies that changed filmmaking, from green screens to CGI.
- Is anything truly original? – Explore the concept of originality in art and whether all ideas build on what came before.
- Why anime went global – Trace anime from Astro Boy to Spirited Away to global streaming dominance. Discuss what makes anime aesthetically distinct, how it influenced Western animation, and why it resonates across cultures.
- Video games as an art form – Examine high-budget games as creative works and compare them to film and traditional art.
- Why songs get stuck in your head – Explain the science of earworms and what makes certain melodies so persistent.
- Modern mythology – Identify contemporary myths and urban legends and explore why people believe them.
Fun informative speech topic ideas

These topics are light and entertaining but still educational. They're great for engaging an audience that wants to learn something unexpected.
- The wildest conspiracy theories – Tour the strangest modern conspiracies, from flat earth to reptilian elites to suspiciously abundant mattress stores. Break down the psychological and social forces that keep these beliefs alive—without endorsing them.
- The truth about UFOs – Revisit famous sightings, leaked footage, and recent government disclosures. Separate speculation from evidence and explain what scientists actually think is going on.
- How magic tricks really work – Unpack the psychology and techniques behind classic illusions: misdirection, forcing, sleight of hand. Explore why understanding the method doesn’t completely kill the wonder.
- Unsolved mysteries that still baffle us – Present eerie cases that remain unexplained, along with the most compelling theories and why none fully satisfy.
- The history of timekeeping – From sundials to atomic clocks, trace how humans learned to measure time. Explain time zones, leap seconds, and why GPS satellites need relativity to function.
- Declassified government experiments – Share surprising programs that were once secret and are now public, and what they reveal about power, ethics, and Cold War paranoia.
- The weirdest laws still on the books – Highlight bizarre laws across the U.S. and beyond, where they came from, and why they technically still exist.
- The world’s most ridiculous sports – From cheese rolling to wife carrying, explore competitions that sound fake but are taken very seriously by real athletes.
- How cultures celebrate major life moments – Compare wedding, birth, and funeral traditions around the world and what they reveal about values and belief systems.
- Breakfast around the world – Take a culinary tour of what people eat first thing in the morning—and why sweet breakfasts are actually pretty unusual globally.
- Humans vs. animals: who really wins? – Compare strength, speed, senses, endurance, and intelligence across species, and see where humans surprisingly dominate—or totally lose.
- The origin stories of famous memes – Trace where iconic memes came from, how they mutated, and why some images conquer the internet while others disappear instantly.
- Why we make bad decisions – Explore the psychology behind poor judgment, risky behavior, and overconfidence, with examples everyone recognizes in themselves.
- The history of the selfie – Follow self-portraiture from royal paintings to bathroom mirrors, and how technology reshaped vanity, identity, and documentation.
- A day in the life of a bizarre job – Walk through a lesser-known career and what the work actually involves, from skills required to unexpected hazards.
- Foods that can kill you if prepared wrong – Examine dishes like fugu, casu marzu, and ackee fruit. Explain the chemistry behind the danger and why people still seek them out.
- Words that don’t translate cleanly – Explore terms from other languages that capture emotions or experiences English struggles to express.
- Do personality tests actually work? – Review the science behind Myers-Briggs, the Big Five, and other popular assessments, and why people love them anyway.
- The science of happiness – Look at what research says truly increases happiness—and which common assumptions are mostly myths.
- How animals communicate – Explore how different species share information, from chemical signals to body language, and what counts as “language.”
- Foods with a fake health halo – Reveal the nutrition realities behind foods that sound healthy but often aren’t, and why marketing works so well.
- The science of first impressions – Explain how quickly we judge others, what those snap judgments get wrong, and why they’re so hard to undo.
- The history of the handshake – Trace how this simple gesture became a global norm, how it differs across cultures, and why it keeps disappearing and returning.
- Urban wildlife: animals that mastered cities – Explore how certain species adapted to human environments and what their success says about evolution.
- Which diets actually work long-term? – Compare popular diets and what the evidence shows about sustainability, health, and why most people regain the weight.
- The data behind online dating – Analyze surprising patterns from dating apps, including what actually predicts success and which profiles people say they want versus choose.
- Why humans love ranking everything – From top-10 lists to tier charts, explore our obsession with ordering the world and what it does to how we think.
Conclusion
Preparing for a speech can feel overwhelming, but choosing the right topic makes everything easier.
Hopefully this list serves as a good source of inspiration. And once you're ready to build your slides, try Plus AI to create a first draft and get moving faster.